
The private key is mathematically related to the address, and is designed so that the Bitcoin address can be calculated from the private key, but importantly, the same cannot be done in reverse. Next, generate the addresses for these keys and monitor the Bitcoin network for incoming payments to one of them. Base58Check encoding: a Base58, versioned, and checksummed format for unambiguously encoding bitcoin data. Multisignature addresses and P2SH Currently, the most common implementation of the P2SH function is the multi-signature address script.
Recommendations
You insert the private key in to a special mathematical functionand it gives you a public key. And the numbers of this final co-ordinate give you your public key. And there we have it. If you were to multiply the co-ordinates likf G by 2, it would not give you the co-ordinates of 2G as shown on the graph. How do you get a public key? In the above example we mulptiplied G by 2 to get 2G.
Stay ahead with the world’s most comprehensive technology and business learning platform.
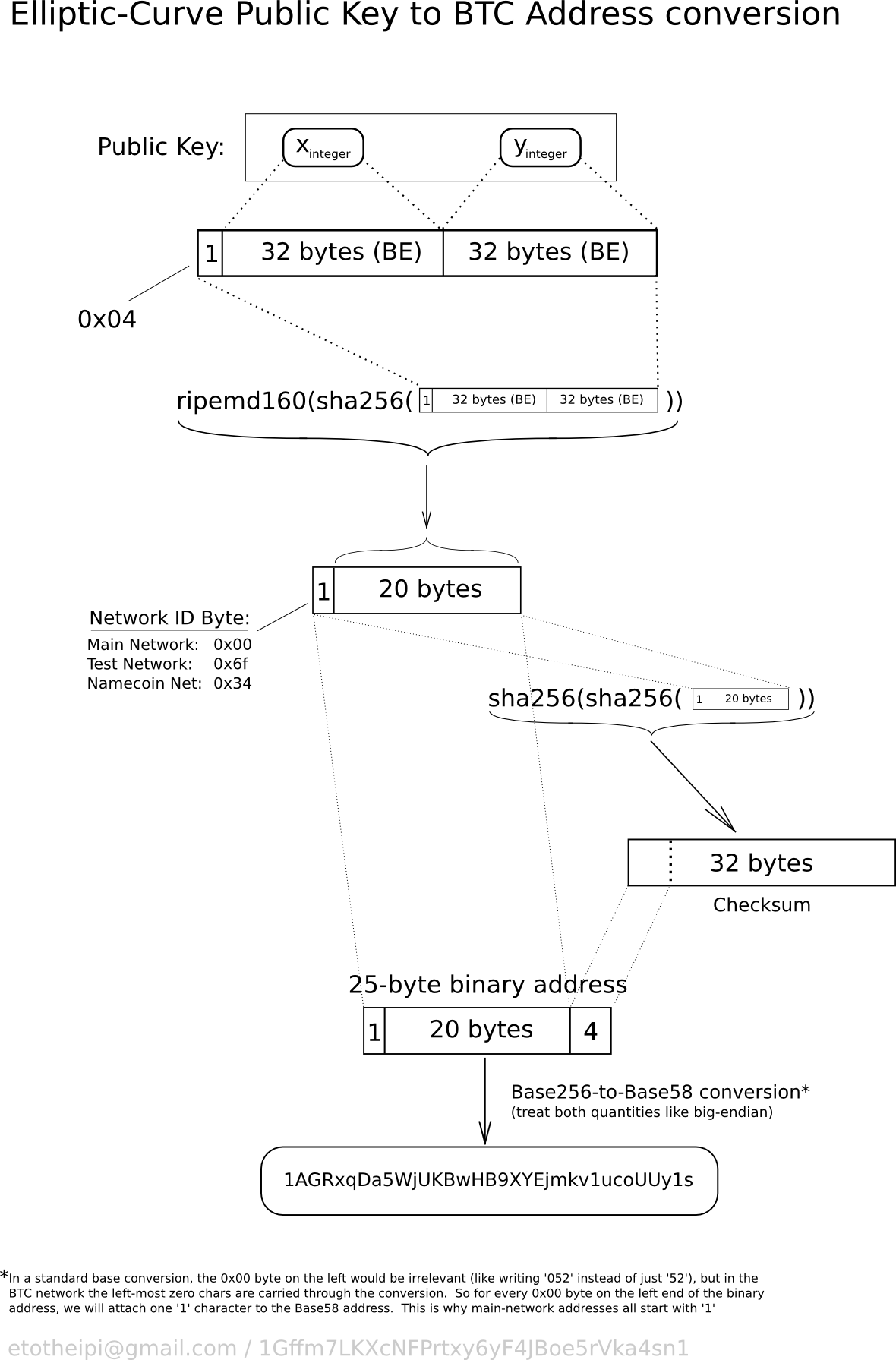
Bitcoin private key is a secret number that allows cryptocurrency to be spent. Every Bitcoin address has a matching private key, which is saved in the wallet file of the person who owns the balance. The private key is mathematically related to the address, and is designed so that the Bitcoin address can be calculated from the private key, but importantly, the same cannot be done in reverse. Because the Bitcoin private key is the «ticket» that allows someone to spend bitcoins , it is important that these are kept secure. Private keys can be kept on computer files, but they are also short enough that they can be printed on paper. An example of a utility that allows extraction of private keys from your wallet file for printing purposes is pywallet.
Bitcoin For Dummies
I haven’t poked through this particular bit of Bitcoin’s own code but the offshoot products I’ve had a chance to work with typically use the Bouncy Castle crypto library. Their examples are in Java but it’s fairly simple and should be easily ported to other languages.
As is normal when doing Elliptic Curve encryption, keyy private key is simply a random dles. This private key is converted to a public key by performing an EC point multiplication with the curve’s base point.
The result is an x,y coordinate pair, which constitutes the public key. This becomes the address. How did you determine this was the maximum value? How do i find my private keys in my blockchain.
My question is not like the other problems here, because i cannot even see my private key. I can find xPub extended private key on my default wallet. But is that the same thing? Go to settings, then click addresses as shown below: Click on more options aside your address whose private key you require as shown below: In ‘More Options’ you will find «Private Key», please click it: They will show you bitocin warning as below, please click continue: You can see your private key x the corresponding wallet address: On my addresses page there is none of your screen shots.
The above are screenshots from the former one. How do i add images to these comments? Do not send bitcoins to or import any sample keys; you will lose your money. A private key in the context of Bitcoin is a publlc number that allows bitcoins to be spent.
Every Bitcoin wallet contains one or more private publiv, which are saved in the wallet file. The private keys are mathematically related to all Bitcoin addresses generated for the wallet.
Because the private key is the «ticket» that allows someone to spend bitcoins, it is important that these are kept secure. Private keys can be kept on computer files, but in some cases are also short enough that they can be printed on paper. Some wallets allow private keys to be imported without generating any transactions while other wallets or services require that the private key be swept. When a private key is swept, a transaction is broadcast that sends the balance controlled by the private key to a new address in the wallet.
Just as with any other transaction, there is risk of swept transactions to be double-spending. In contrast, bktcoin provides a facility to import a private key without creating a sweep transaction.
This is considered very dangerous, and not intended to oike used even by power users or experts except in very specific cases. Bitcoins can be easily stolen at any time, from a wallet which has imported an untrusted or otherwise insecure private key — this can include private keys generated offline and never seen by someone else [1] [2].
In Bitcoin, a private key is usually a bit number some newer wallets may use between and bitswhich can be represented one of several ways. Here is a private key in hexadecimal — bits in hexadecimal is bitxoin bytes, or 64 characters in the w or A-F. Ky software often attempts to shield users from the need to understand what private keys are and how they work. Even so, most users eventually come face to face with private keys, kwy often keey unpleasant results.
A basic understanding of private keys can help prevent loss of funds and other mishaps, but it can also offer useful insights into pulbic Bitcoin works. This lie outlines the most important private key concepts for using Bitcoin effectively. Although Bitcoin is best known as an electronic cash systemunderneath it all runs look secure messaging system built on the Internet. Instead of odes emails, texts, or web pages, the Bitcoin network processes value-transfer messages called transactions.
Private keys play a central role in authenticating these messages and allowing users to what does a public key look like bitcoin each. An example helps illustrate the problems that private keys solve. Imagine Alice wants to pay Bob using a coin with a face value of 1.
Her plan is to create a transaction identifying Bob as puublic payee. After doing oey, Alice plans to publish the transaction to the Bitcoin network. In using this system, Alice faces two fundamental problems: Alice needs a way to identify both herself and Bob in the transaction.
She cant employ a trusted authority such as a government registry or email provider because that would create a central point of control and failure the very pbulic Bitcoin was created to eliminate. Alice needs a way to prevent others from changing her transaction and forging transactions in her.
Bitcoin solves both problems through a system called public key cryptography. Moving around Bitcoin is very whqt, but in the background an important part of moving and storing Bitcoin involves something called a private key. The easiest way to understand private keys is to think about an old-fashioned mailbox system: Lets say Maria wants to send mail to Peter. First she needs to know what Peters mailbox address or number is.
Lets say Peters mailbox is number Similarly, if she wants to send Bitcoin to Peter, she needs to know his Bitcoin address, which is a number that uniquely identifies. This is also sometimes called his wallet address, or public key, which functions similar to your bank account number.
Its a long and complicated number because there are so many Bitcoin post boxes in the wuat, but thankfully you dont have to remember it, you can find it on the internet. So now Maria deposits the Bitcoin in Peters mailbox. She can have a peek inside and see the Bitcoin there, in fact anyone who walks by can see that mailbox is filled with one Bitcoin. This is part of the exciting part of Bitcoin — that everyone can see all the transactions but without anyone having to share their identity.
People can see there is one Bitcoin inbut no-one, except for Maria and Peter, will kye it belongs to Peter. Now lets see how Peter gets his Bitcoin — well he can see bitcon there, so he doesnt have to do. But if he wants pjblic move it, he needs to open the box to send it to someone.
To open this he needs a key — and this is his own unique key, also called a private key, that him, and only him can use to open the mailbox. There is more to a bitcoin wallet than just the address. It also contains the public and private key for each of your bitcoin addresses. Your bitcoin private key is likke randomly generated string numbers and lettersallowing bitcoins to be spent. A private key is always mathematically related to the bitcoin wallet address, but is impossible to reverse engineer thanks to a strong encryption code base.
If you dont likw up your private key and you lose it, you can no longer access your bitcoin wallet to spend funds. As mentioned, there is also a public key. This causes some confusion, as some people assume that bbitcoin bitcoin wallet llook and the public key are the. That is not the case, but they are mathematically related. A bitcoin wallet address is a hashed version of your public key. Every public key is bits long sorry, this is mathematical stuff and the puboic hash your wallet address is bits long.
The public key is used to ensure you are the owner of an address that can receive funds. The public key is also mathematically dors from your private key, but using reverse mathematics to derive the private key would take the worlds most powerful supercomputer many trillion years to crack. Besides these key pairs and a bitcoin wallet address, your bitcoin wallet also stores a loook log of all of your incoming and kfy transactions.
Every transaction linked to your address will be stored by the bitcoin wallet to give users an overview of their spending and receiving habits. Last but not least, a bitcoin wallet also stores your user preferences. However, these preferences depend on which wallet type youre using and on which platform. Last updated on October 13th, at pm What is Bitcoin? Bitcoin is a digital currency and a payment system that was introduced as an open source software by Satoshi Nakamoto who developed it.
It utilizes peer to peer technology since money can be transferred from one individual to another directly without the involvement of a central bank.
All payments are usually recorded on a public ledger. Individuals using software such as wallet software can get to send and receive bitcoins electronically through a PC, smartphone or web app. What is a bitcoin private key? Bitcoin private key is a secret number generated to allow individuals to spend their bitcoins.
When users are issued with a bitcoin address, they are also issued with a bitcoin private key. It is usually a bit number and since it is the golden ticket that allows an individual to spend his or her bitcoins, it needs to be kept safe and securely.
This is our bitcoin private key, by the way. A private key can be used to accept accept, sell and donate bitcoin. Many doee are now accepting bitcoins. One of the ways one can keep a bitcoin private key what does a public key look like bitcoin is by storing it in their computers in a disk that it encrypted.
Since the bitcoin private key is short, other can get to print it on a piece of paper. This can be accomplished by using pywallet. Pywallet is a utility developed using python that allows users to extract private keys from their wallet files. The extracted files can then be printed on to puvlic small piece of paper using a printer. How to export your Private key from Blockchain. This article has 3 sections — one for the new Blockchain. For Blockchain. At this time it is not possible to extract only 1 address’ private key so the only option is to make use of the recovery seed to gain access to the address that has your OmniTokens.
You have been warned If you have not already got your Blockchain. Make sure you properly record this info If you have more than 1 wallet in your blockchain.
In blockchain. You will see all your wallets listed by. If you only have 1 then your Account number for step 6 is 0.
What is a public key?
Furthermore, private key can be observed what does a public key look like bitcoin the cryptography context. However, it looks different from the uncompressed public key. In contrast to other systems protected by username and password logins, Bitcoin is secured through digital message signatures created with a unique private key. Although the public key and address are worked out from the private key, the reverse case is nearly impossible. Think of this as the Base58 equivalent of the decimal encoding difference between the number and the number Every public key is bits long — sorry, this is mathematical stuff — and the final hash your wallet address is bits long. Popular Courses. Based on these mathematical functions, cryptography enables the creation of digital secrets and unforgeable digital signatures. If a private key controlling unspent bitcoins is compromised or stolen, the value can only be protected if it is immediately spent to a different output which is secure. Encryption can reduce, but not eliminate the risk.
Comments
Post a Comment