No centralized «official» copy exists and no user is «trusted» more than any other. By design, a blockchain is resistant to modification of the data. Blockchains can serve as a fully transparent and accessible system of record for regulators. Put in the simplest terms, the quest for decentralised trust has quickly become an environmental disaster. Here are some of the most popular applications of blockchain being explored today.
Blockchain
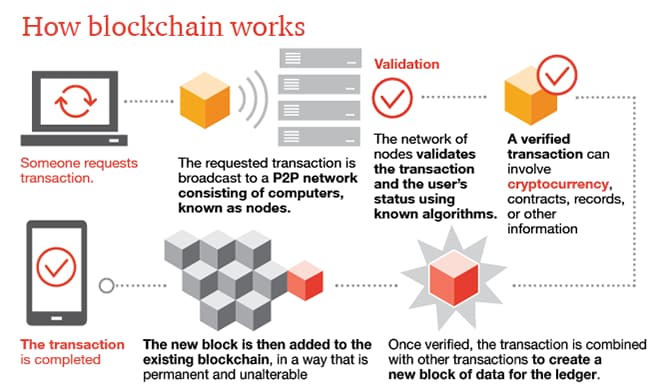
A Blockchain is a way of linking encrypted digital records that is used as the basis of the modern digital economy. Blockchains what does blockchain mean bitcoin a decentralized record of transactions that can be verified by a network of independently operated servers. This allows for transactions between two parties that do not necessarily know or trust each other without the need to have a third-party step in to mediate. In recent years blockchain technology has evolved by leaps and bounds, and its potential uses have radically expanded. This includes the development of what is called Blockchain 2. Today there are hundreds of different blockchain based companies, currencies, and applications that are using the technology in increasingly innovative ways.
Why is it Called “Blockchain”?

A blockchain is a public ledger of information collected through a network that sits on top of the internet. It is how this information is recorded that gives blockchain its groundbreaking potential. Blockchain technology is not a company, nor is it an app, but rather an entirely new way of documenting data on the internet. The technology can be used to develop blockchain applications, such as social networks, messengers, games, exchanges, storage platforms, voting systems, prediction markets, online shops and much more. The information recorded on a blockchain can take on any form, whether it be denoting a transfer of money, ownership, a transaction, someone’s identity, an agreement between two parties, or even how much electricity a lightbulb has used.
TED Talks: The Blockchain Explained Simply
Giving Thought
Hence, anything that is built on the blockchain is by its very nature transparent and everyone involved is accountable for their actions. Explore how others might try to disrupt your business with blockchain technology, and how your company could use it to leap ahead instead. Enjoy a free lesson from the Blockgeeks Library! Ethereum itself is a platform for smart contract code. The blockchain network has no central authority — it is the very definition of a democratized. Netki is a startup that aspires to create an SSL standard for the blockchain. Major portions of the financial industry are implementing distributed ledgers for use in banking[57] [58] [59] and according to a September IBM study, this is occurring faster than expected. Retrieved 17 January However, in a peer-to-peer system, there is no central authority, and hence if even one of the peers in the network goes out of the race, you still have more peers to download. The popularity of these sites suggests people want to have a direct say in product development. Blockchain Reaction: How library professionals are approaching blockchain technology and its potential impact. Archived from the original on 8 November Retrieved 19 June From greater user privacy and heightened security to lower processing fees and fewer errors, blockchain technology may very well what does blockchain mean bitcoin applications beyond those outlined. Alternatively, to prevent a permanent split, a majority of nodes using the new software may return to the old rules, as was what does blockchain mean bitcoin case of bitcoin split on 12 March How is the Lisk blockchain governed?
Comments
Post a Comment