In other words, in a deflationary environment, goods and services decrease in price, but at the same time the cost for the production of these goods and services tend to decrease proportionally, effectively not affecting profits. Active 1 year, 7 months ago. Eventually, once all the 21 million possible Bitcoins are mined, miners will rely entirely on these fees for their income.
When Will the Last Bitcoin be Mined?
Bitcoin miner fees are small amounts of bitcoin given to incentivize bitcoin miners and their incentivjses to confirm bitcoin transactions. Bitcoin miners are the special pieces of hardware that confirm and secure transactions on the bitcoin network. Miner fees pay miners for the service they provide. Miner fees do not go to BitPay. Bitcoin miners confirm and secure transactions by adding blocks to the blockchain.
News feed continued
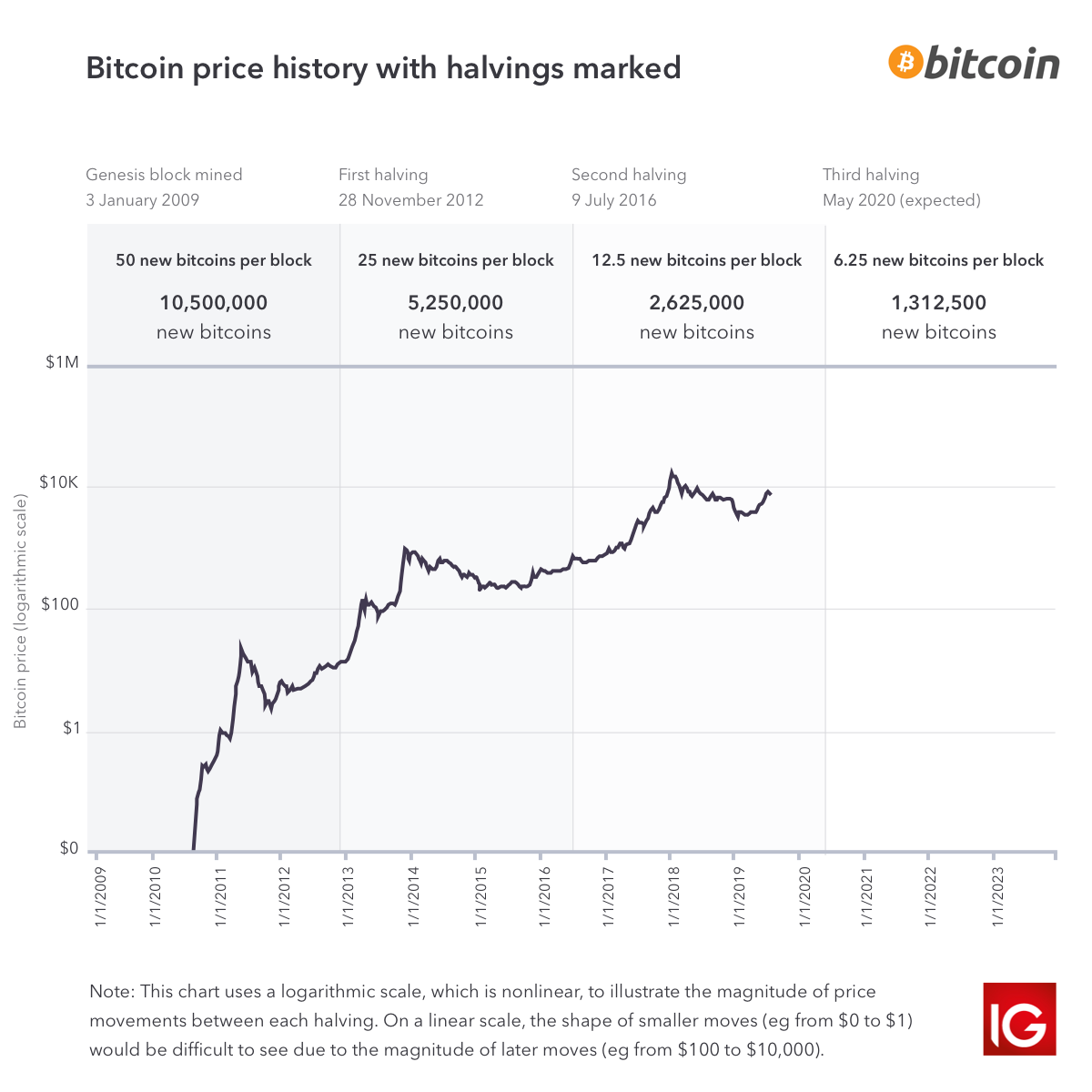
Bitcoin is like gold in many ways. Like gold, bitcoin cannot simply be created arbitrarily. Gold must be mined out of the ground, and bitcoin must be mined via digital means. Linked with this process is the stipulation set forth by the founders of bitcoin that, like gold, it must have a limited and finite supply. In fact, there are only 21 million bitcoins that can be mined in total. Once miners have unlocked this many bitcoins, the planet’s supply will essentially be tapped out, unless bitcoin’s protocol is changed to allow for a larger supply.
Name that Crypto! https://t.co/ymYaBDdgM6 pic.twitter.com/Yvu6lQgWgB
— Jason Fernandes (@TokenJay) October 18, 2019
Bitcoin’s Mining Rules
The short answer is that Bitcoin is a cryptocurrency or digital asset made secure by cryptography. Bitcoin and most but not all other cryptocurrencies use blockchain technology. This article will answer the common questions that newcomers have when first learning about Bitcoin. How do blockchains work?
What makes Bitcoin valuable? Ater is decentralization? What is mining? How do you buy Bitcoin? How do you safely store it? How do you send or receive Bitcoin from somebody else?
There may be blockchain-related terms in this article that you are unfamiliar. Keep reading and see if the context helps clear things up.
If you want to make sure you understand everything more thoroughly, you can also refer our guides to essential blockchain and cryptocurrency terms. There are many different cryptocurrencies out there that serve different purposes. Bitcoin is the first and most well-known cryptocurrency, but not all cryptocurrencies necessarily resemble Bitcoin. At its most fundamental level, a cryptocurrency is simply a peer-to-peer digital payment.
Another way to say peer-to-peer is that there is no middleman — specifically banks or financial institutions — that facilitate transactions. For a more in-dept explanation, read our article What is Cryptocurrency? Now, on to Bitcoin! Dreated Bitcoin whitepaper was published in by a pseudo-anonymous author named Satoshi Nakamoto.
It was the first time ever that somebody put together the ideas of a digital currency and blockchain technology. People have been speculating about the true identity of Nakamoto ever. As the original Bitcoin miner, he is known to have amassed approximatelybitcoins. Those coins have remained untouched for years, and it seems likely that they will forever stay out of circulation. Satoshi Nakamoto was last heard from way back in early Many have tried to ade him since, but to no avail thus far.
Notably, the first block Nakamoto mined — called the genesis block — contained a message. This references a news article about the government bailouts of banks during the economic recession. It is widely accepted to be a political statement by Nakamoto about the reason Bitcoin was created — to disrupt the financial institutions that have long controlled our economies and livelihoods.
Bitcoin first began gaining some significant adoption in Wikileaks and other organizations began accepting Bitcoin donations, and it was mentioned occasionally in pop culture. Bythere were over 1, merchants accepting Bitcoin. Then, in FebruaryMt Goxthe largest cryptocurrency exchange at the time, filed for bankruptcy after havingbitcoins stolen.
Still, more and more businesses began accepting Bitcoin, including tech giants Microsoft and Dell. For most of that time, currencies were backed by gold. However, that gitcoin changed during the 20th century, with many countries being forced off the gold standard as a result of the Great Depression.
That leaves the question: what are fiat currencies backed by now, if not gold? What makes Bitcoin different from fiat currencies is simply a matter of where that trust is placed. For fiat, the trust is placed in people-run institutions.
For Bitcoin, nitcoin trust is placed in rceated — the blockchain. The innovation that makes Bitcoin possible is blockchain technology. A blockchain is a digital ledger of information that can be easily distributed across a network. It is what makes Bitcoin accessible to anybody with internet access, anywhere in the world.
Each block in a blockchain contains data. Once a block is added to the blockchain, it can never be removed or otherwise altered incentivixes any way. Bitcoin transactions, once validated, are permanent. New transactions are processed and validated by miners. More on how mining works later. Most systems that govern human society are centralized. Governments, banks, and corporations are typically structured such that the majority of the decision-making power is concentrated at the top.
Large databases are typically stored and maintained in data centers at only one or two locations. Blockchains enable us to run systems without concentrating power over those systems in the hands of a small minera of minera populations that ccreated. They enable us to store databases simultaneously in hundreds or even thousands of different locations. This is called incentivisfs.
In database terms, decentralized systems have improved security because they do not have a single point of failure. In other words, if a handful of the locations storing a blockchain suddenly go offline for some reason, there are still hundreds of others doing the work.
The system continues on without so much as a hiccup. Of course, many centralized systems still have good security. Is there more to decentralization than just distributing databases? Yes, there is. Decentralized systems are designed so that every participant can act in their own best self-interest within the system without harming other participants. No individual has power or control over the. This is what incentivises bitcoin miners after all bitcoin are created makes blockchain technology truly revolutionary.
Bitcoin may just be a bunch of computer code, but it still takes humans to run that code. More accurately, it takes humans to build and maintain the machines that run the code. These machines and the people who operate them are called miners. Perhaps the most critical obstacle that Satoshi Nakamoto needed to navigate when designing Bitcoin was figuring out how to get miners to run the network without giving them additional power to control it. With game theory in mind, Nakamoto devised a brilliant solution.
A blockchain minus the incentives is just a distributed digital ledger, minus the trustless security. A distributed digital ledger would be helpful to efficiently connect various manufacturers, warehouses, and stores.
Miners that process transactions need incentives to do so honestly. Otherwise, they could add invalid transactions to the blockchain, giving themselves more money.
Blockchain miners have the role of processing new transactions and minting new digital coins. They do this by periodically adding new blocks containing transactional data to the blockchain. Individual miners compete to find the solution to a difficult cryptographic puzzle. Once the solution is found, the miner is able to propose a new block to add to the end of the blockchain. When a block is proposed, other miners check whether it is valid or invalid. If the block is valid, the other miners will add it to the blockchain and begin competing to propose the next block.
Mlners valid blocks might be proposed almost simultaneously, or perhaps some percentage of the miners will purposely accept an invalid block to benefit themselves. However, there is only one valid blockchain — the longest chain with the most blocks. Now imagine that those miners decide to try to benefit themselves dishonestly by posting invalid transactions. One of the who solves the cryptographic puzzle first would propose a block with the invalid transactions, and the other would accept it what incentivises bitcoin miners after all bitcoin are created begin adding more blocks to it.
Instead, they would be adding to a chain of valid blocks. Having three times the mining power of the dishonest group, the would add new blocks to their branch of the blockchain three times as fast. That would give them bitcoij longest chain, accepted by all users.
The other chain would become worthless and no users would accept it. Anything short of that, and the malicious activity will be unsuccessful. For a blockchain to be trustless, two things must be true about its miners:. Miners do, however, have the ability to propose a new block to the blockchain even if it contains invalid transactions.
The idea behind Proof-of-Work is to make it extremely expensive to mine, discouraging malicious mining activities such as posting blocks with invalid transactions. And, to the contrary, the idea behind block rewards is to make it profitable to mine if you do so honestly.
The Bitcoin protocol has built-in computational wastefulness. But all of that computation craeted electricity just the same as the useful computation. Electricity consumption costs money, making it expensive to. The purpose of that wastefulness is to disincentivize miners from being dishonest. If it succeeds, they gain a lot. The trade-off is certainly worthwhile. Instead, because it is expensive to mine, every malicious attempt comes at a significant cost.
That cost serves as a deterrent from even trying to post malicious transactions.
What Will Happen After We’ve Mined ALL The Bitcoin?
What is Bitcoin mining?
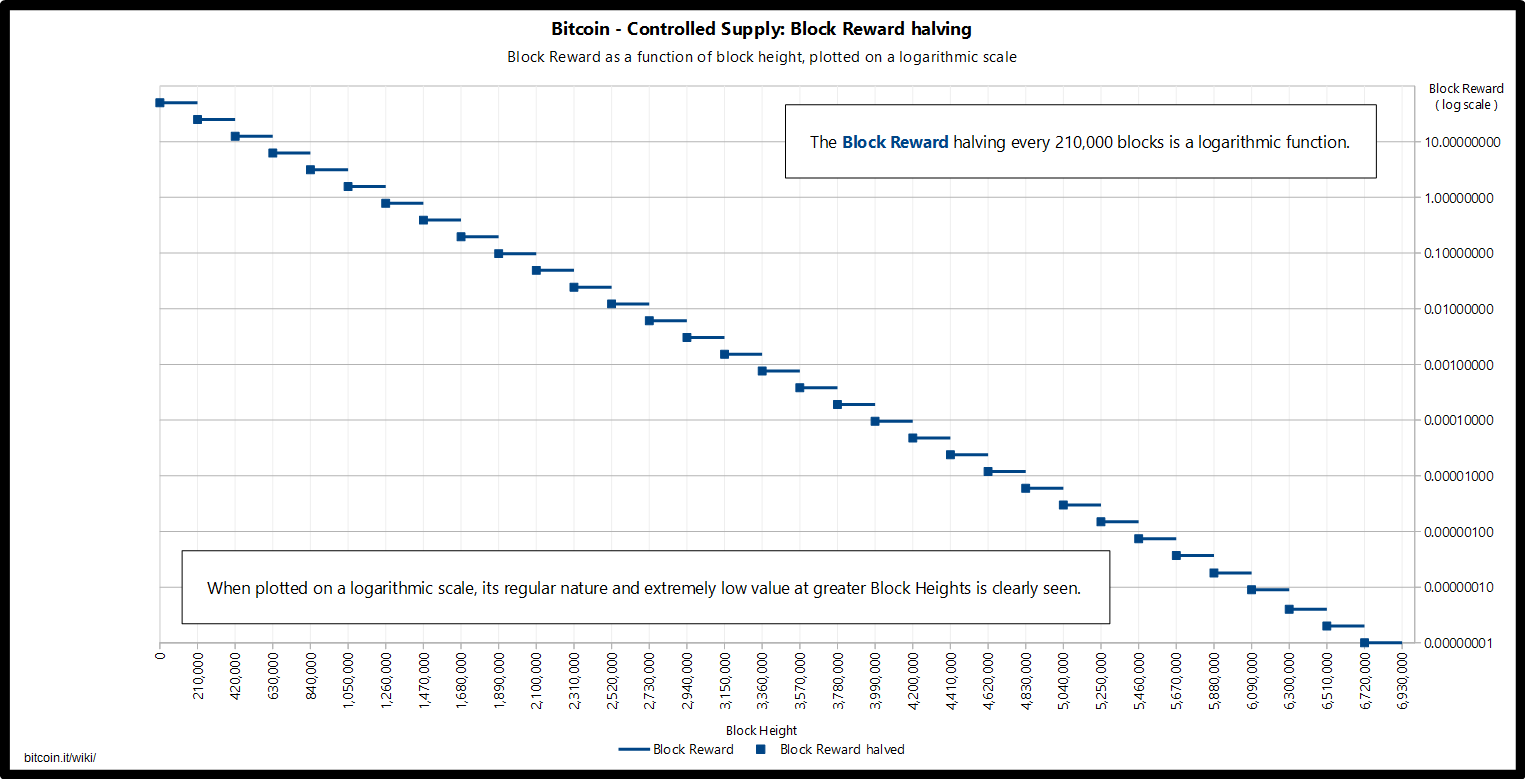
Bitcoins are created each time a user discovers a new block. Then, in an act of sheer stupidity, a more recent miner who failed to implement RSK properly destroyed an entire block reward of Furthermore, since the block reward gradually diminishes dreated time, rather than disappearing all at once, miners have the chance to gradually adapt and adjust to relying more on transaction fees than revenue from mined bitcoins. The theoretical total number of bitcoins, slightly less than 21 million, should not be confused with the total spendable supply. Share to facebook Share ,iners twitter Share to linkedin. Bitcoin is celebrated by supporters and admonished by skeptics because of its finite supply. Due to deep technical reasons, block space is a scarce commoditygetting a transaction mined can be seen as purchasing a portion of it. It may also be the case that transaction fees simply rise to a level sufficient for mining profitability. In older versions of the bitcoin reference code, a miner could make their coinbase transaction block reward have the exact same ID as used in a previous block [3]. This practice leaves gold in the bank, forcing people to trust the bank to handle their gold responsibly. Miners have historically shown a willingness to maintain or increase computing power through halving events because they expect future bitcoin price increases to offset the reduced block reward. For example, if you made a transaction to an address that requires a private key in order to spend those bitcoins further, had written that private key down ae a piece of paper, but that piece of paper was lost. Help me understand. One way to see a part of the destruction of coin is by collecting a sum of all unspent transaction outputs, using a Bitcoin RPC command gettxoutsetinfo.
Comments
Post a Comment