Another option is to import the seed into a compatible HD wallet, such as Electrum. Full report advanced. Facebook Messenger. Great Article! Learn how your comment data is processed. Tweet However, it is not enough to simply know what each of these forks are.
Get the Latest from CoinDesk
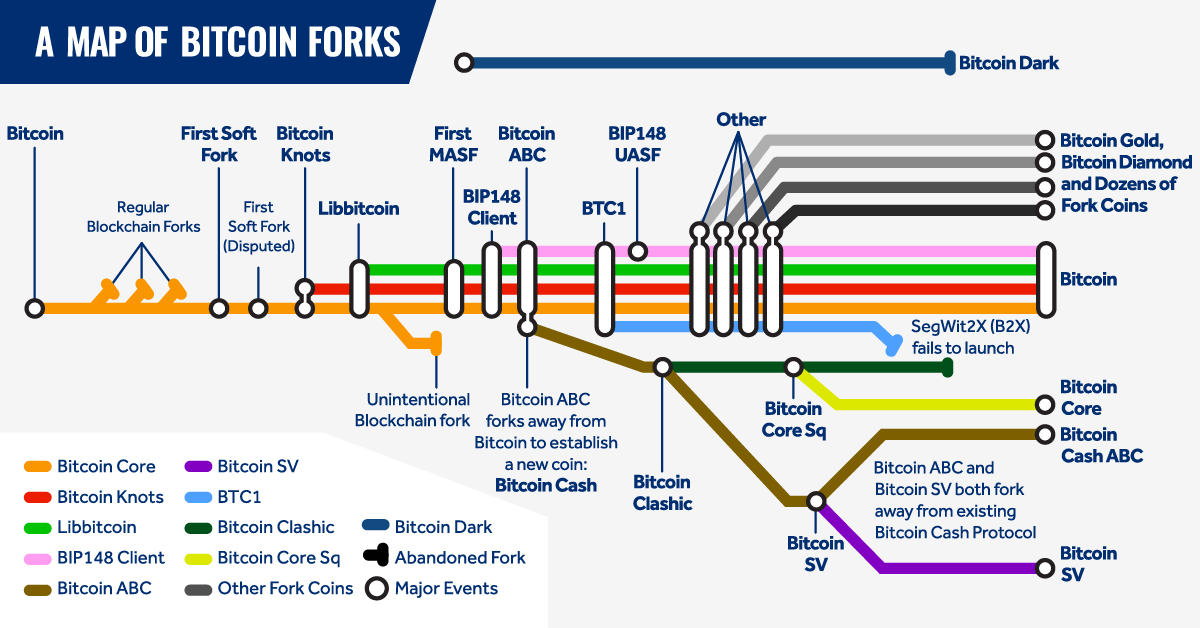
Bitcoin forks are defined variantly as changes in forsk protocol of the bitcoin network or as the situations that occur «when two or more blocks have the same block height». Forks are typically conducted in order to add new features to a blockchain, to reverse the effects of hacking or catastrophic bugs. Forks require consensus to be resolved or else a permanent split emerges. The following fogks forks of the software client for the bitcoin network :. All three software clients attempt to increase transaction capacity of the network.
Welcome to Blockgeeks

Not like the kind you would find on a table, on a blockchain, a fork is a technical event that occurs because diverse participants need to agree on common rules. Yet, there are many different types of forks, and the science of studying them is still new. So far, we know some forks resolve on their own, but others, fueled by deep rifts in a community, can cause a network to permanently split, creating two blockchain histories — and two separate currencies. Along with that, there has also been confusion about the various types of forks, how they get activated and the risks they pose. A byproduct of distributed consensus, forks happen anytime two miners find a block at nearly the same time.
Join Bitcoin Community
Not like the kind you would find on a table, on a blockchain, a fork is a technical event that occurs because diverse participants need to agree on common rules. Yet, there are many different types of forks, and the science of studying them is still new. So far, we know some forks resolve on their own, but others, fueled by deep rifts in a community, can cause a network to permanently split, creating two blockchain histories — and two separate currencies.
Along with that, there has also been confusion about the various types of forks, how they what coins are bitcoin forks activated and the risks they pose. A byproduct of distributed consensus, forks happen anytime two miners find a block at nearly the same time. But forks also can be willingly introduced to the network. This occurs when developers seek to change the rules the software uses to decide whether a transaction is valid or not.
When a block contains invalid transactions, that block is ignored by the network, and the miner who found that block loses out on a block reward. As such, miners generally want to mine only valid blocks and build on the longest chain. What is it? You can think of a hard fork as an expansion of the rules. What happens? Nodes that continue running the old version of the software will see the new transactions as invalid. So, to switch over to the new chain and to continue to mine valid blocks, all of the nodes in the network need to upgrade to the new rules.
What can go wrong? The problem comes when some sort of political impasse arises, and a portion of the community decides to stick by the old rules no matter. The hash rate, or network computing power, behind the old chain is irrelevant. What matters is that its data and ruleset is still perceived to have value, meaning miners still want to mine a chain and developers still want to support it. The ethereum DAO hard fork was a perfect case study of how a community can split over rules.
Now, we have two blockchains using a variant of the software — ethereum and ethereum classic, both of which boast a different ethos and a different currency. Say, instead of 1MB blocks, a new rule might only allow K blocks. Non-upgraded nodes will still see the new transactions as valid k is less than 1MB in this example. However, if non-upgraded nodes continue to mine blocks, the blocks they mine will be rejected by the upgraded nodes.
This is why soft forks need a majority of hash power in the network. When a soft fork is supported by only a minority of hash power in the network, it could become the shortest chain and get orphaned by the network. Or, it can act like a hard fork, and one chain can splinter off. The idea with UASF is that instead of waiting for a threshold of support from mining pools, the power to activate a soft fork goes to the exchanges, wallets and businesses who are running full nodes.
In bitcoin, a full node, even if it is not a mining node, is still responsible for validating blocks. The majority of major exchanges would need to publicly support the change before it could be written into a new version of code. After that, the new software which has an activation point in the future gets installed on nodes that want to participate in the soft fork.
This method requires a much longer lead time to work than a hash-power-triggered soft fork. Table setting via Shutterstock. The leader in blockchain news, CoinDesk is a media outlet that strives for the highest journalistic standards and abides by a strict set of editorial policies.
CoinDesk is an independent operating subsidiary of Digital Currency Group, which invests in cryptocurrencies and blockchain startups. A Short Guide to Bitcoin Forks. As a result, those who use the blockchain have to show support for one choice over the. Following are some of the more common forks and their traits. Hard fork What is it? User-activated soft fork What is it? Currently this idea is theoretical and has not been implemented.
Read more about Disclosure Read More The leader in blockchain news, CoinDesk is a media outlet that strives for the highest journalistic standards and abides by a strict set of editorial policies.
Markets Daily. Adam B. Levine Bradley Keoun Dec 17, Year in Review
Welcome to Blockgeeks
Ckins a fork does not implement replay-protection, you are vulnerable to replay attacks when you transfer coins on either chain. Obvious Ehat propaganda article. Hard forks splitting bitcoin aka «split coins» are created via changes of the blockchain rules and sharing a transaction history with bitcoin up to a certain time and date. The average hashrate plummeted around 29th and 30th April and then picked right up. Bitcoin Mining, Explained Breaking down everything you need to know about Bitcoin mining, from blockchain and block rewards to Proof-of-Work and mining pools. You also know the difference between soft and hard fork. Those opcodes being:. Hidden categories: Wikipedia indefinitely semi-protected pages. Inshortly after releasing bitcoin, Satoshi mined the first block on the bitcoin blockchain. This feature would be called Segregated Witness aka Segwit. Suppose you are running MS Excel in your laptop and you want to open a spreadsheet built in MS Excelyou can still open it because MS Excel is backward compatible. ICOs vs. The tool or wallet will regenerate the private keys and their addresses, which allows this info to be imported to the fork-coin in the what coins are bitcoin forks format.
Comments
Post a Comment